肿瘤|JITC:华科同济医学院的这个肠癌疗法厉害了!( 二 )
文章图片
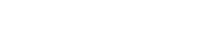
患者治疗前后的免疫组化结果
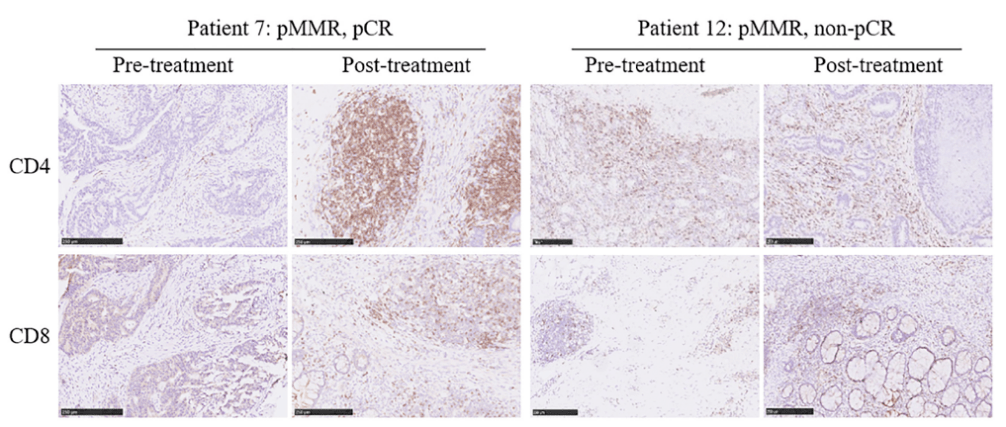
研究者们也对治疗方案的安全性进行分析 , 治疗过程中出现的不良反应如下表所示 。 主要的不良反应为白细胞减少(80%) , 反应性皮肤毛细血管内皮增生(73.3%)及放射性直肠炎(70%) 。 免疫相关的不良反应主要为1-2级 。 在治疗过程中未出现因严重不良反应所致的死亡事件 。
文章图片
入组患者治疗过程中的不良事件
最后 , 研究者对14名pMMR患者的组织样本进行二代测序 , 发现肿瘤组织中最常见的基因突变为 TP53 、 APC 及 KRAS, 由于样本量偏小 , 测序未发现pCR及非pCR患者中有基因存在显著表达差异 。 但 相比肿瘤突变负荷(TMB)<10的患者 , TMB≥10的患者pCR有升高趋势(TMB≥10, 42.9%, 3/7;TMB<10, 28.6%, 2/7, p=0.3671) 。
尽管既往研究表明pMMR患者在肿瘤免疫治疗中获益有限 , 但本研究的上述结果提示 ,高TMB的pMMR结直肠癌患者 , 也可能从免疫治疗中获益 , 患者TMB水平或有助于预测联合方案的新辅助治疗效果 。
文章图片
部分入组患者的二代测序结果
总体来说 , 术前低分割SCRT+化疗+免疫治疗的综合新辅助治疗方案 , 在本次研究中对LARC患者达到较好的pCR率 , 而pCR率的提高往往意味着患者的长期预后改善 。 不过也要注意的是 , 本研究毕竟是一项小样本研究 , 缺乏随机对照且随访时间短 , 应用价值仍需要后续的大样本研究进行证实 。

文章图片
参考文献:
1.Sineshaw, H.M., et al., Changes in treatment patterns for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer in the United States over the past decade: An analysis from the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer, 2016. 122(13): p. 1996-2003.
2.Feng, R.M., et al., Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics? Cancer Commun (Lond), 2019. 39(1): p. 22.
3.Lin, Z., et al., Phase II, single-arm trial of preoperative short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy and camrelizumab in locally advanced rectal cancer. J Immunother Cancer, 2021. 9(11).
6.Erlandsson, J., et al., Optimal fractionation of preoperative radiotherapy and timing to surgery for rectal cancer (Stockholm III): a multicentre, randomised, non-blinded, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol, 2017. 18(3): p. 336-346.
7.Bahadoer, R.R., et al., Short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy before total mesorectal excision (TME) versus preoperative chemoradiotherapy, TME, and optional adjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer (RAPIDO): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol, 2021. 22(1): p. 29-42.
【肿瘤|JITC:华科同济医学院的这个肠癌疗法厉害了!】8.Sharabi, A.B., et al., Radiation and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy: radiosensitisation and potential mechanisms of synergy. Lancet Oncol, 2015. 16(13): p. e498-509.
- 脏腑|重庆肿瘤专科医院:中医帮你调和气血,平衡阴阳
- 预防肿瘤|夜里温度下降孩子睡不好,多吃营养菜,补虚暖胃,提高抵抗力
- 致癌|十多种肿瘤与“吃”密切相关,看完请注意避开!
- 肿瘤|健康大讲堂丨肿瘤专家袁芃:乳腺癌病因尚不明确 防治重在“三早”
- 香港|广州复大肿瘤医院案例966:香港胰腺癌患者赴广州就医重获新生
- 胶质瘤是脑内最常见的恶性肿瘤之一|胶质瘤能治好吗?复发后有必要再次手术吗?医生说了实话
- 关注 癌症的死亡率高、治愈率低|科普|八桂中医大讲堂(4):中西医结合治疗恶性肿瘤有哪些优势?
- 肝左叶|专家携手为早产儿切除少见巨大肝脏肿瘤
- 常吃这7类食物易患肿瘤
- 肿瘤|肿瘤患者到底能不能拍CT?还可以做什么检查,看看你就知道了